Folliculitis and Hair Removal: What to Know and How to Prevent It
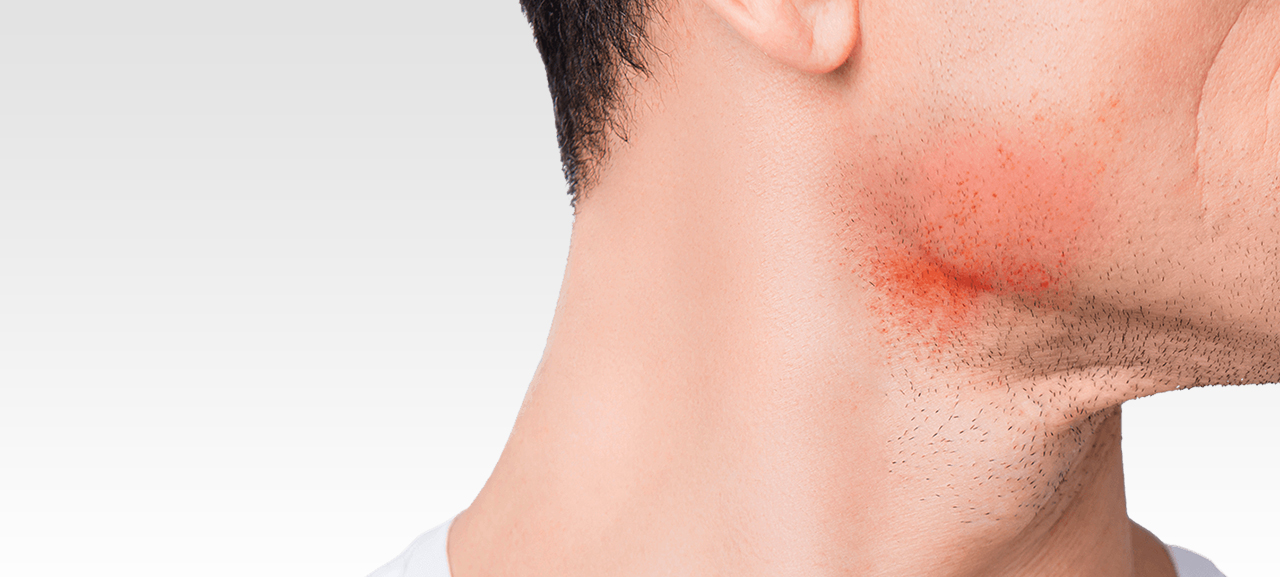
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles, often caused by bacterial infections, blockages, irritation, or certain dermatological conditions. This condition can arise for various reasons, including ingrown hairs, and typically appears as small red bumps or white pimples around hair follicles. Folliculitis may be superficial or deep, depending on the severity of the inflammation and its spread into the dermis.
In severe cases, folliculitis lesions can evolve into non-healing wounds or pus-filled pustules, which, if manipulated, risk leaving scars and hairless areas. One of the most common forms of folliculitis is due to shaving or waxing, which can range from superficial to deep.
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae and Sycosis Barbae
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is a superficial folliculitis from shaving, affecting mainly men with curly hair who shave very closely, leading to ingrown hairs and irritation. Women who wax the bikini area may also develop this condition, which can leave dark, raised scars. Sycosis barbae, on the other hand, is a deeper form of folliculitis where the infection spreads, triggering a more intense autoinflammatory response.
How to Prevent Folliculitis
Here are some tips to prevent folliculitis during shaving or hair removal:
– Gentle Shaving: Shave in the direction of hair growth, using an electric razor or clean, sharp blades. Avoid pressing the razor too firmly.
– Moisturize the Skin: Use shaving gel or foam instead of soap, which can dry out the skin.
– Shower and Bath: Perform hair removal at the end of a shower to soften the skin and remove dead skin cells.
– Regular Exfoliation: Remove dead skin cells to prevent ingrown hairs and reduce follicle blockage.
– Wear Suitable Clothing: Avoid tight clothing right after shaving, and wash promptly if sweating occurs.
Permanent hair removal, such as laser hair removal, can reduce the risk of folliculitis in more sensitive areas.
Folliculitis Treatment
If folliculitis or pseudofolliculitis is present:
– Avoid Shaving: Refrain from shaving for extended periods in recurrent cases (up to three months if necessary).
– Topical Creams: A doctor may prescribe cortisone creams or Vitamin A-based treatments (like tretinoin) to manage inflammation and follicular hyperkeratosis.
– Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation Treatment: Hydroquinone or other skin-lightening creams can help reduce hyperpigmentation.
– Antibiotics for Infections: For bacterial infections, targeted antibiotic therapy may be recommended, possibly chosen through culture and sensitivity testing.
In mild cases, folliculitis can resolve on its own with proper precautions and cool compresses to soothe inflammation. It’s essential to use clean towels until fully healed and avoid squeezing pustules to prevent permanent scarring.



